Home
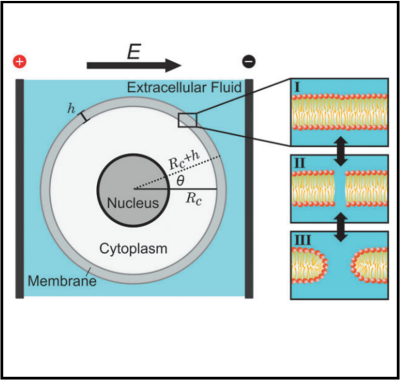
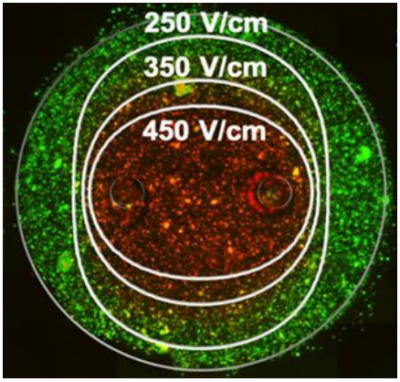
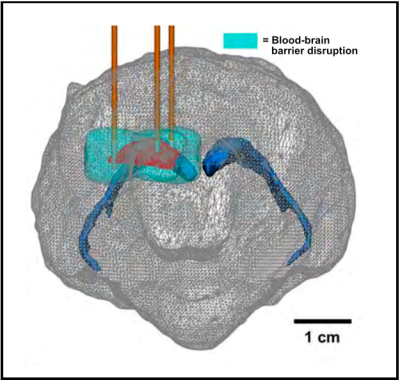
Bioelectromechanical Systems (BEMS) Lab is a cross disciplinary group that investigates the electrical properties of biological systems, from the cellular to organ level, for aplication in cancer and cardiac ablation treatments. Our lab focuses on using pulsed electric fields (PEFs) to generate nanoscale pores in the cell membrane, termed electroporation. This can be used to deliver chemotherapeutics, genes, or other otherwise impermeable substances into target cells. Further, we develop a technology termed irreversible electroporation, where we use larger electric fields to generate pore sizes past the point where cells can maintain homeostasis. This allows us to kill cells in target tissue without thermal effects, preserving proteneous structures like ducts, myelinated cells, and blood vesssels. This technology, invented and developed by Dr. Davalos, is currently being used in clinic for the treatment of aggressive, non-resectable pancreatic cancer, but we are currently developing the next generation for better treatment of soft tissue tumors, like liver, prostate, pancreas, prostate, and brain cancer.
RESEARCH AREAS
Location
Virginia Tech: ICTAS Stanger Street, Blacksburg, VA
Available Facilities and Resources:
Bioelectromechanical Systems Lab
The laboratory of Davalos is located in the new ICTAS Research Facility on campus. The room is approximately 2,000 square feet and contains all the necessary equipment to conduct the experiments. Capabilities include a benchtop test facility, equipped with an inverted Leica DMI6000 epifluorescence microscope equipped with dual pass filters; remote control; ac and dc high voltage power supplies; plasma cleaner for bonding microfluidic chips; automated signal generation equipment; a desktop computer to control the equipment and record data; EM-CCD camera and a digital camera; tools for electrical wiring: two infusion/withdraw micro syringe pumps to control the flow rate of biological samples in the microfluidic channels precisely; a Lynx stereo microscope that significantly increase head freedom and eye relief; microcentrifuge, PH meter, conductivity meter, a function generator and oscilloscope, wideband amplifier, a high voltage transformer, a lock in amplifier for ultra low voltage measurements, refrigerator, hood, incubator, and freezers(-4°C and -20°C). The laboratory also has an ECM BTX Electroporation system to conduct experiments on suspensions and tissue phantoms.
Nanofabrication and Characterization Laboratory (NCFL)
The NCFL at Virginia Tech houses state-of-the-art nanometrology equipments, which includes an environmental SEM (FEI Quanta 600 FEG) and an FIB SEM (FEI Helios 600 NanoLab) with cryo transfer system (PolarPrep 2000). The E-SEM is used for imaging biological specimens at pressures as low as 4000 Pa, while the FIB SEM with cryogenic stage is useful for imaging surface and cross-sectional features of biological materials.
Computers
The microscope station has a dedicated computer for data acquisition and analysis. There is another computer in the lab for high performance computing and image analysis. The computers are equipped with high-speed Internet connection and contain a variety of software, such as Adobe Photoshop, data acquisition software, MATLAB, and FEMLAB. In addition to these computers, the PI has a computer to aid in data analysis and presentation.
PI: Rafael V. Davalos, Ph.D.
L. Preston Wade Professor
ASME Fellow, Coulter Fellow, AIMBE Fellow
CV
329 ICTAS Stanger Street (0298)
Blacksburg, VA 24061
(540) 231-1979


